Overview of the modules interactionsLink
The following figure shows a use case of the ROMI modules, and the way they interact, to design an efficient plant phenotyping platform used in research.
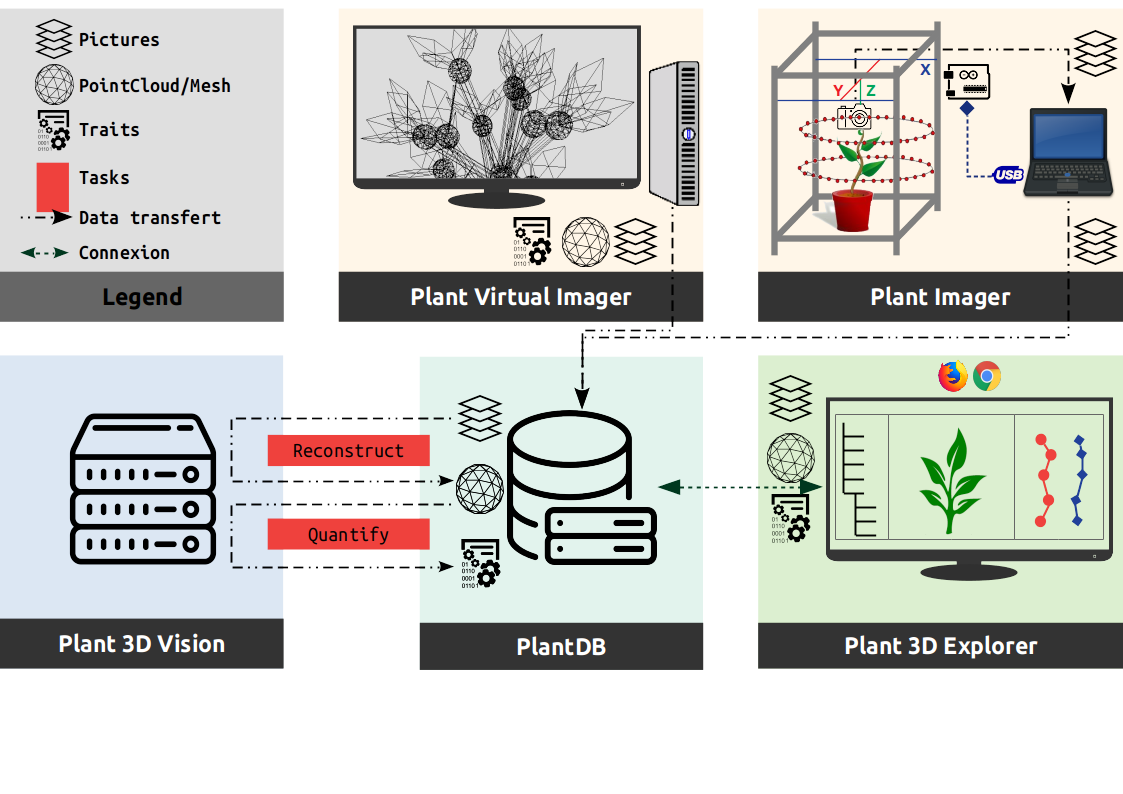
PlantDBLink
It implements our database system and is totally independent of the rest since it could be uses in other parts of the ROMI project (Rover, Cable bot, ...) through the abstract class DB or even the local database class FSDB.
Plant ImagerLink
It requires a physical connection to the hardware (pyserial) to control.
It also needs an active ROMI database (PlantDB) to export acquired datasets (plant images).
Virtual Plant ImagerLink
It requires a connection to an active ROMI database (PlantDB) to export generated datasets (virtual plant images). In case of machine learning methods, the database would also provide training datasets and trained models.
Plant 3D VisionLink
It requires connection to an active ROMI database (PlantDB) to import the dataset to process and export the results. Two plant reconstruction approaches are available:
- Geometry based: try to infer the plant's geometry using structure from motion algorithms and space carving to first reconstruct a point cloud.
- Machine learning based: try to infer the plant's geometry using semantic (organ) segmentation of pictures and space carving to first reconstruct a labelled point cloud.
Then meshing and skeletonization finally enables to extract the plant's phyllotaxis.
Plant 3D ExplorerLink
It requires an active ROMI database (PlantDB) with datasets to browse and represent.